Advance persuasion skills for professionals who want to excel in their life.
Most business decisions are made on the basis of rapport rather than technical merit
You are more likely to buy from, agree with, and support someone you can relate to than someone you can't - People like people who are like themselves.
When people are trusting and comfortable with each other, barriers come down and interesting things happen. They begin to stand, sit, move or sound like each other. They take on each other's posture, movements or voice expressions, and breathing patterns. If one moves, the other may soon follow.
But as a business person, how many times have you been amazed at how communication can go badly wrong? How easy it is for the slightest gesture or tone of voice to be taken the wrong way.
Neuro-Linguistic Programming began with the study of excellent communicators. What is the difference that makes the difference in feeling comfortable and acknowledged by someone, even if they are disagreeing with what you say? How is it that some people you meet you instantly like - while others you can't get away from fast enough? Why can you talk to some people for hours and it seems like minutes?
 The answer to all of these questions is rapport - a foundation stone of NLP, and the most important process in any communication. Rapport is the ability to enter someone else's world, to make them feel that you understand them, that you have a strong common bond. Rapport is the ability to see each other's point of view (not necessarily to agree with it), to be on the same wavelength and to appreciate each other's feelings. And when you are in rapport something magical happens. You and others feel listened to, and heard. At an unconscious level, there is a comfortable feeling of ' This person thinks like I do, I can relax.'
The answer to all of these questions is rapport - a foundation stone of NLP, and the most important process in any communication. Rapport is the ability to enter someone else's world, to make them feel that you understand them, that you have a strong common bond. Rapport is the ability to see each other's point of view (not necessarily to agree with it), to be on the same wavelength and to appreciate each other's feelings. And when you are in rapport something magical happens. You and others feel listened to, and heard. At an unconscious level, there is a comfortable feeling of ' This person thinks like I do, I can relax.'
Research has shown that in the understanding of a received communication, 7% is contained in the words used, 38% is contained in the tone and style of voice, and 55% is contained in the physiology of the deliverer. Yet how many people actually study the factors which control over half of their communication?
NLP is concerned with what works, rather than what is the most elegant theory. In any interpersonal communication, this means knowing where the other person is coming from - somehow bridging your different perspectives of the world.
NLP has evolved a number of presuppositions, or underlying principles that represent a kind of instinctive wisdom . Four presuppositions are particularly relevant to effective rapport:
The map is not the territory:
We each perceive the world uniquely, as though in possession of an individual map of the real world, one we have charted ourselves. These maps are made of our collection of past experiences, attitudes and beliefs. We tend to filter experience to fit our perceptions and beliefs. True communication, therefore, must attempt to understand other people's perceptual maps. By sharing other maps and adjusting our own from time to time, rapport increases and communication is made more effective.
The meaning of the communication is the response you get:
The purpose of communication, like any behaviour, is to bring about a desired outcome, such as pass on information, to delegate, lead, encourage, influence, or whatever. Unless it fulfils the desired outcome it is ineffective. If the other person does not understand your communication it is probably because you have not put it in terms of their map of the world.

You cannot not communicate:
We are all communicating all the time, most non-verbally. Even our inner thoughts - in effect our internal communications - are often passed on to others, through our posture, body movements, facial expressions, breathing, gestures, voice tone or eye movements.
The mind and body are part of the same system - the NLP Communication Model:
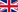
Our thoughts instantly affect our physiology and this in turn affect our thoughts. When something happens outside of us (external event), we take in information through our five senses - what we see, hear, feel, smell and taste. We reduce that information down by filtering through our life’s experiences: delete, distort and generalise and pass the information through our filters: language, memories, decisions, perceptions, values, beliefs and attitudes. That creates an internal representation of the event -the pictures in your head and the way you might talk to yourself. This in turn affects your emotional state -how you feel about it. If you have a good picture you feel great, if you have a bad picture you feel lousy. Those two affect your physiology - thinking, feeling, stance, breathing. Your internal representation, state and physiology become the driving force for your behaviour. Your behaviour becomes the Input into the other person.
Whatever the circumstances or content of your communication outcome, establishing rapport must be high on your agenda. But what is it and how can we do it successfully?
Matching & Mirroring
People in rapport typically adopt the same posture, move and gesture in similar ways, adopt the same style and rhythm in movement and speech. They 'match' or 'mirror' each other. This happens naturally when two or more people are in rapport. They are probably not consciously aware of it happening. The result of this is that their thinking, feelings and behaviour will be similar.
The best communicators match without thinking. This matching may extend to matching of voice - speed, volume and tone, breathing, facial expressions, eye movements.
Communicating with another person whose body language is very different from your own - perhaps sitting with crossed legs and arms in response to your open posture - can be surprisingly difficult. Or imagine a conversation between a slow, reflective talker and a very fast talking person.
Mirroring is physically copying the behaviours of another in a subtle manner. While mirroring is simultaneous with the other person's movements, matching can sometimes have a 'time delay factor to it. For example, if someone is gesturing while talking and making a point. When it is your turn to speak, you can make your comments and your point using the same, or similar gestures.
Language of Senses
In the same way that you can pace and lead a person's body language, voice, so you can pace and lead a person's thinking preferences and language patterns. NLP found that people tell how they are processing information with the words they breathe and the way they move their eyes. Each of us has a thinking preference - to 'think' in images, sounds, or feelings for instance. What's more your speech is an expression of the way you think. For example, if you think visually you are more likely to say: 'I get the picture' or 'I see what you mean' because you do. If, however, you think in an auditory way you would be more likely to say :'I hear you loud and clear' or 'We're on the same wavelength'.
Cross Matching & Mismatching
If the prospect of consciously mirroring is embarrassing or daunting, you can use the concept cross-over matching or mirroring. This is choosing to match one of your behaviours to a corresponding, but different movement of another. For example, if someone folds their arms, cross your legs; or pace the rhythm of someone's speaking with slight nods of your head or your breathing. Mismatching is also a useful skill to master. Have you ever had someone go on and on and on when having a conversation with them? You can break eye contact, turn your body at an angle to them, breathe faster or slower...in short, do anything to break rapport by mismatching. You will be surprised how quickly and easily the conversation will draw to a close.
Sensory Acuity & Calibration
As well as actively matching to increase rapport, by observing the other person for evidence of matching, you can determine the extent to which you have rapport - whether you are connecting, whether they are paying attention. At the simplest level we can deduce from a smile or a frown (or a yawn) what the other person is feeling. The most foolproof way is to first pace the other person and attempt to lead. If they follow you are in rapport. If not you are not.
Pacing & Leading
When we are in rapport we tend to follow a person's physiology when it changes. If the person crosses their arms, there is a good chance that the other person will do the same shortly afterwards.
Using this principle, matching can be used in a more positive and influential way. . For example, persuading a client or colleague who is sceptical, putting someone at ease, getting someone enthusiastic who is lethargic. Having established rapport by pacing you can gradually lead the person the way you want to - subtly lead them into a certain voice mode, facial expression or physiological posture with a view to changing their state of mind, whilst maintaining rapport and then anything is possible.
Personal success and business success relies largely on your ability to communicate. NLP offers you state of the art communication techniques that will enable you to achieve extraordinary results. Rapport is a pre-requisite to good communication, influence and change. What if you could master this skill?